Parameters
ParametricText has basic support for including parameter values using
Python Format
Specifiers.
By writing {parameter}, the text is substituted by the parameter
value. E.g., if the parameter d10 has the value 20, {d10} becomes
20.0. {d10:.3f} becomes 20.000 (3 decimals).
The special parameter _ gives access to special values, such as
document version.
Document Parameters
Both model and user parameters can be used as input for the parametric text. The following properties are accessible.
Property |
Type |
Description |
Example Value |
|---|---|---|---|
parameter.unit |
string |
Parameter unit |
mm |
parameter.expr |
string |
Parameter expression |
25 mm |
parameter or parameter.value |
decimal (double) |
Parameter value |
25.0 |
parameter.comment |
string |
Parameter comment |
Distance between slots |
parameter.inchfrac |
– |
Parameter value as mixed fraction inch |
1 1/2” |
Compare the above properties with the Fusion 360™ parameters dialog, as shown below.
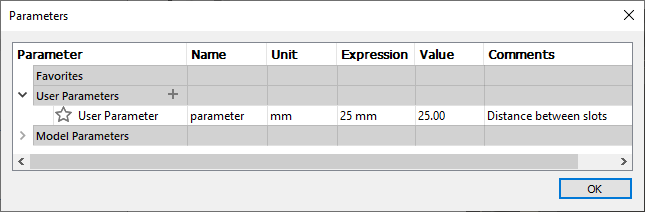
Fusion 360™ Parameters Dialog
The Special Parameter (_)
ParametricText includes a special parameter, _, that does not exist in the Fusion 360™ parameters dialog. _ provides values from the document and its content.
Property |
Type |
Description |
Example Value |
|---|---|---|---|
_.component |
string |
Name of the component containing the text |
Component1 |
_.compdesc |
string |
Description of component containing the text |
Complex Description in the Component |
_.partnum |
string |
Part number of component containing the text |
123-AB |
_.configuration [1] |
string |
Name of the active configuration |
Configuration 2 |
_.date [2] |
datetime |
Date & time when the file was saved |
2021-07-06 |
_.file |
string |
Name of the document/file |
My File |
_.newline |
– |
Breaks the text into a new line |
↵ |
_.sketch |
string |
Name of the sketch containing the text |
Sketch1 |
_.version |
string |
Document version |
10 |
Parameter Formatting
ParametricText has basic support for including parameter values using
Python Format Specifiers, allowing for things such as zero-padding or
a fixed number of decimals. E.g. {d10:.3f} will show the value of
d10 with 3 decimals.
Refer to Format Specification Mini-Language for the full set of options.
Examples
Input variable value |
Expression |
Example Result |
Explanation |
|---|---|---|---|
d10 = |
|
10.000 |
Parameter value with 3 decimals |
d10 = |
|
10 |
Parameter value without decimals |
_.version = |
|
002 |
Document version, expressed with 3 digits, with zero- padding. |
Date Formatting
_.date supports Python strftime() formatting. E.g., {_.date:%Y} will show the year that the document was saved.
Refer to strftime() and strptime() Format Codes for the full set of options.
Examples
Expression |
Example Result |
Explanation |
|---|---|---|
|
2020-09-27 |
ISO 8601 format |
|
09/27/2020 |
Month/day/year |
|
40 |
Current week, that starts on a Sunday |
|
39 |
Current week, that starts on a Monday |
|
14:58 |
Hour:minute in 24-hour format |
Substrings
String parameter values (e.g. _.file, _.component,
``parameter``.comment) can be cut into substrings using the
Python slice notation: [start:stop] (the step option is not
supported).
The range is left-inclusive and right-exclusive, meaning that a range of
[2:4] will give the characters at index 2 and 3, but not 4.
The character position is zero-indexed, which means that the first
character will be number 0.
Note: The length of numeric parameters can be adjusted using the Python Format Specifiers instead of substrings.
Examples
Expression |
Example Result |
Explanation |
|---|---|---|
|
My |
First two characters of the document name |
|
m |
The third character of the component name |
|
slots |
Last five characters of d10’s comment |
|
een slots |
The fourteenth character and on |